The Growth of Plastic Production Over the Years
How Much Plastic is Produced Annually?
Global plastic production has seen an astronomical rise since the 1950s. In 2022, the world produced over 400 million metric tons of plastic. This figure represents a 1.6% increase from the previous year, underscoring the continued growth in plastic production. The versatility of plastic makes it a highly sought-after material.
Historical Trends in Plastic Production
The first synthetic plastic, Bakelite, was created in 1907. However, it wasn't until the 1950s that plastic production began its rapid ascent. Annual production has increased nearly 230-fold to 460 million tonnes by 2019. Even in just the last two decades, production has doubled, highlighting the accelerating pace of plastic manufacturing.
Global Plastic Production by Year
In 1950, the world produced a mere two million tonnes of plastic. This number has surged to over 400 million tonnes annually. The Our World in Data website provides a detailed graph of this increase. This demonstrates the dramatic growth of the plastics industry over the past seven decades.
Plastic Production Statistics: 2022 and 2023
In 2022, global plastic production reached 400.3 million metric tons. While 2023 data is still preliminary, it is expected to show a continued upward trend. The Plastics Europe organization provides a snapshot of these figures in their "Plastics – the fast Facts" report. This ongoing increase highlights the challenges of managing plastic waste.
Plastic Production Statistics 2024: What to Expect?
While complete data for 2024 is still being compiled, it is projected that plastic production will remain high. The demand for plastic across various industries continues to drive this growth. Factors such as packaging needs, construction, and automotive applications contribute to the increasing production rates.
Regional Leaders in Plastic Production
Asia is the world's largest producer of plastics. China alone accounts for about 32% of global production. North America ranks second, with a 17% share in 2022. These regional disparities highlight the varying levels of industrialization and consumption patterns around the world.
The Role of Plastic Packaging in Overall Production
A significant portion of plastic production is dedicated to packaging. Approximately 36% of all plastics are used in packaging. This includes single-use items like food and beverage containers. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) notes that about 85% of this packaging ends up in landfills or as unregulated waste.
The Environmental Impact of Plastic Production
Annual Plastic Waste Generation
The world generates approximately 350 million tonnes of plastic waste each year. This vast quantity of waste poses a significant environmental challenge. Only a small fraction is recycled, with the majority ending up in landfills or the environment. This highlights the need for better waste management strategies.
The Issue of Mismanaged Plastic Waste
A large portion of plastic waste is mismanaged, meaning it's not recycled, incinerated, or kept in sealed landfills. This mismanaged waste is at a high risk of polluting the environment. Our World in Data shows that about one-quarter of plastic waste is mismanaged. This makes it vulnerable to leaking into ecosystems.
Plastic Waste in Oceans
Between 1 and 2 million tonnes of plastic enter the oceans every year. This represents about 0.5% of the total plastic waste generated. UNEP estimates that 75 to 199 million tonnes of plastic are already in our oceans. This influx of plastic poses a severe threat to marine life and ecosystems.
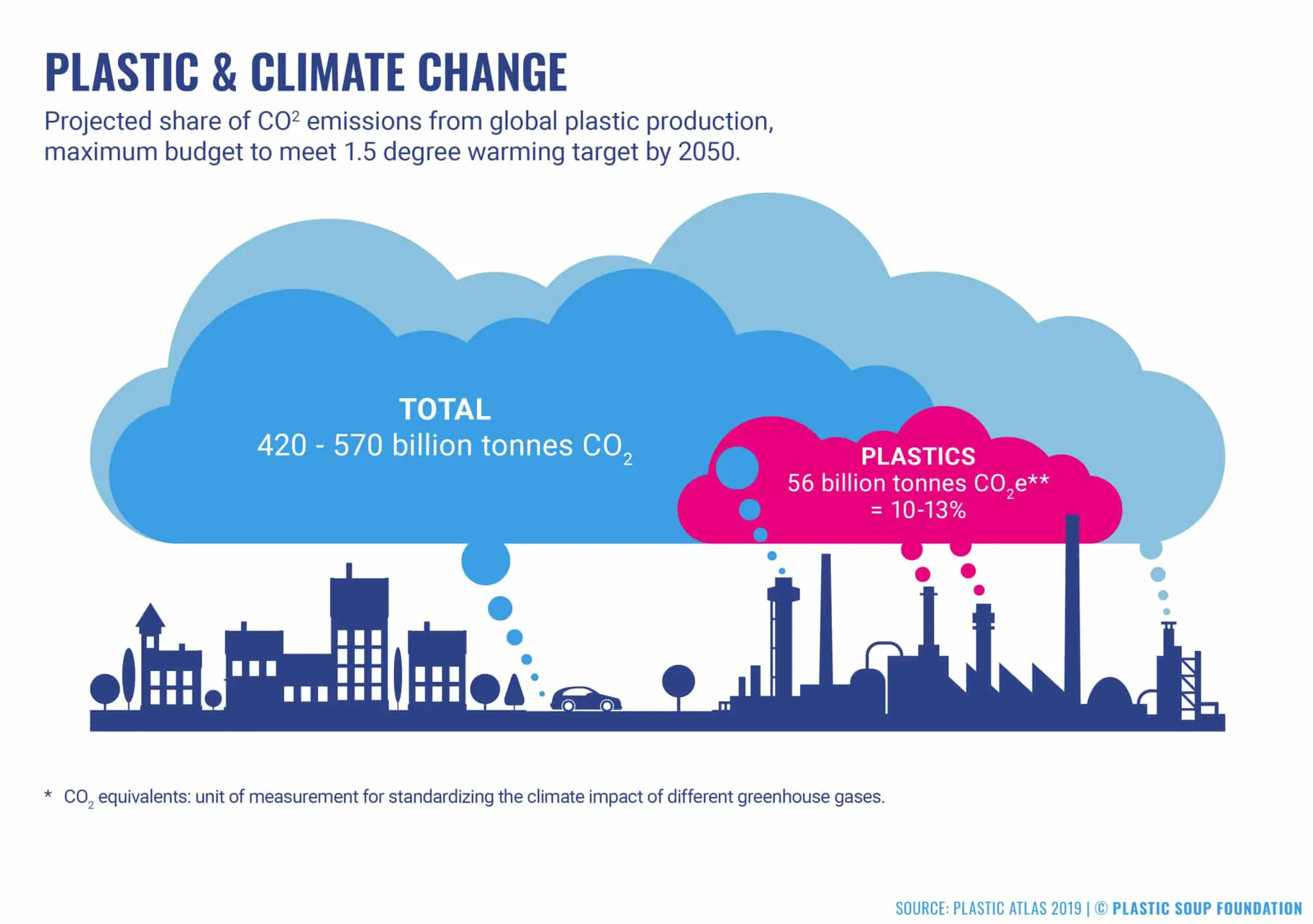
The Link Between Plastic Production and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The production of plastic is heavily reliant on fossil fuels. About 98% of single-use plastics are made from "virgin" fossil fuel feedstock. The greenhouse gas emissions from plastic production, use, and disposal are projected to reach 19% of the global carbon budget by 2040, according to UNEP. This link underscores the need to shift towards more sustainable materials and production methods.
The Persistence of Plastics in the Environment
Plastics are incredibly durable and resistant to degradation. This means they can persist in the environment for centuries. Most plastic items break down into smaller pieces known as microplastics. These microplastics can enter the food chain and even the human body. This persistence makes plastic pollution a long-term environmental problem.
Future Trends and Predictions for Plastic Production
The Future of Plastic Production 2025 and Beyond
Global plastic production is projected to reach 1,100 million tonnes by 2050, if current trends continue. This increase underscores the urgent need for sustainable alternatives and better waste management. The Statista website provides a forecast of this growth. This highlights the scale of the challenge ahead.
The Push for a Circular Economy for Plastics
The concept of a circular economy is gaining traction in the plastics industry. This approach focuses on minimizing waste and promoting the recycling and reuse of plastics. Companies are now designing products for recycling and opting for materials that can be efficiently processed. This shift is crucial for reducing the environmental impact of plastics.
Biodegradable Plastics and Their Role
Biodegradable plastics are emerging as a potential solution to mitigate plastic pollution. These plastics are designed to break down more quickly in the environment. They can be made from ordinary polyethene and polypropylene with special additives. This addresses the issue of long-lasting plastic waste.
Innovations in Plastic Recycling
Innovations in plastic recycling are crucial for creating a circular economy. These include both mechanical and chemical recycling processes. Mechanical recycling maintains the polymer structure while chemical recycling breaks it down into basic building blocks. Advanced recycling technologies are essential for handling more complex plastic waste.
The Impact of Regulatory Frameworks on Production
Governments and international organizations are implementing stricter regulations to manage plastic waste. These include restrictions on single-use plastics and mandates for recycled content. Such policies aim to push the industry towards more sustainable practices. These regulations are a significant driver of change in the plastics sector.
The Role of Smart and Anti-Microbial Plastics
The development of smart plastics that offer added functionality is also a growing trend. These include plastics that are insect-repellent or rodent-deterrent. Anti-microbial plastics, designed to kill bacteria and viruses, have also become prominent. These innovations showcase the versatility and potential of plastics in various applications.
Addressing the Plastic Problem
The Need for Better Waste Management Strategies
Improving waste management is crucial for tackling plastic pollution. This involves enhancing recycling infrastructure, reducing mismanaged waste, and promoting the use of recycled materials. Our World in Data emphasizes that better waste management is key to ending plastic pollution.
Initiatives to Reduce Plastic Waste
Numerous initiatives are being launched to reduce plastic waste. These include campaigns to eliminate single-use plastics, promote recycling, and encourage the use of reusable alternatives. The U.S. Plastics Pact is an example of a collaborative effort to address plastic waste. These initiatives highlight the collective action needed to tackle this problem.
The Role of Governments, Industries, and Individuals
Addressing plastic pollution requires a multi-faceted approach. Governments need to implement effective regulations and policies. Industries must innovate and adopt sustainable practices. Individuals can reduce their plastic footprint by making conscious choices. This collective effort is essential for creating a sustainable future.
The Importance of Innovation and Collaboration
Innovation and collaboration are key to addressing the plastic problem. This includes developing new materials, improving recycling technologies, and fostering partnerships between stakeholders. Such efforts are crucial for driving real change and creating a circular economy for plastics.
Key Takeaways:
- Plastic production has increased dramatically since the 1950s, reaching over 400 million metric tons annually.
- A significant portion of plastic is used in packaging, contributing to high waste generation.
- Mismanaged plastic waste is a major source of pollution, particularly in oceans.
- The shift towards a circular economy and the development of biodegradable plastics are crucial for sustainability.
- Collective action from governments, industries, and individuals is essential to address the plastic problem.
This blog post also includes relevant internal links, such as Understanding the 7 Types of Plastic and Their Environmental Impact, to provide further context and information to the readers.
