How Solar Panels Can Boost Crop Yields and Food Security
Understanding the Intersection of Solar Energy and Agriculture
Definition of Food Security in the Context of Agriculture
Food security is a critical aspect of human well-being. It ensures that all people have consistent access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food.
This access is essential for maintaining an active and healthy life. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) highlights four key components: availability, access, utilization, and stability.
Overview of Solar Energy and Its Role in Modern Farming
Solar energy is the most abundant renewable energy source on Earth. It is harnessed using photovoltaic (PV) panels that convert sunlight into electricity.
In modern farming, solar energy powers various processes. This enhances food security by providing a sustainable and reliable energy source.
Benefits of Integrating Solar Panels with Agricultural Practices
Economic Advantages for Farmers
Reduced Energy Costs and Increased Profit Margins
Solar panels significantly reduce energy costs for farmers. Once installed, they have low maintenance costs and can generate electricity for decades.
Farmers can save on fuel costs by switching from diesel-powered pumps to solar-powered ones. This increases their profit margins.
Financial Independence and Long-term Savings
Solar energy offers financial independence. Farmers are less affected by fluctuating energy prices.
They can produce their own electricity. This makes their energy costs more predictable and manageable.
Environmental Benefits
Reduction of Carbon Footprint
Using solar energy reduces the carbon footprint of agricultural operations. Traditional farming often relies on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Solar energy provides a clean alternative. It helps to combat climate change.
Promotion of Sustainable Farming Practices
Solar energy supports sustainable farming practices. Solar-powered irrigation systems can optimize water use.
Solar dryers can efficiently process crops without relying on fossil fuels. This reduces environmental impact.
Enhancing Crop Yields and Resource Efficiency
Improved Irrigation through Solar-Powered Systems
Solar-powered irrigation systems provide a sustainable solution for watering crops. These systems are beneficial in remote areas with limited grid access.
They ensure a reliable water supply. Farmers can maintain crop yields even during dry periods.
Contribution to Soil Conservation and Biodiversity
Integrating solar panels with farming can enhance soil health. For example, farming techniques that revive ecosystems and boost soil health often involve practices that are complemented by the presence of solar panels.
The shade from panels can reduce soil erosion. It also promotes biodiversity by creating favorable microclimates.
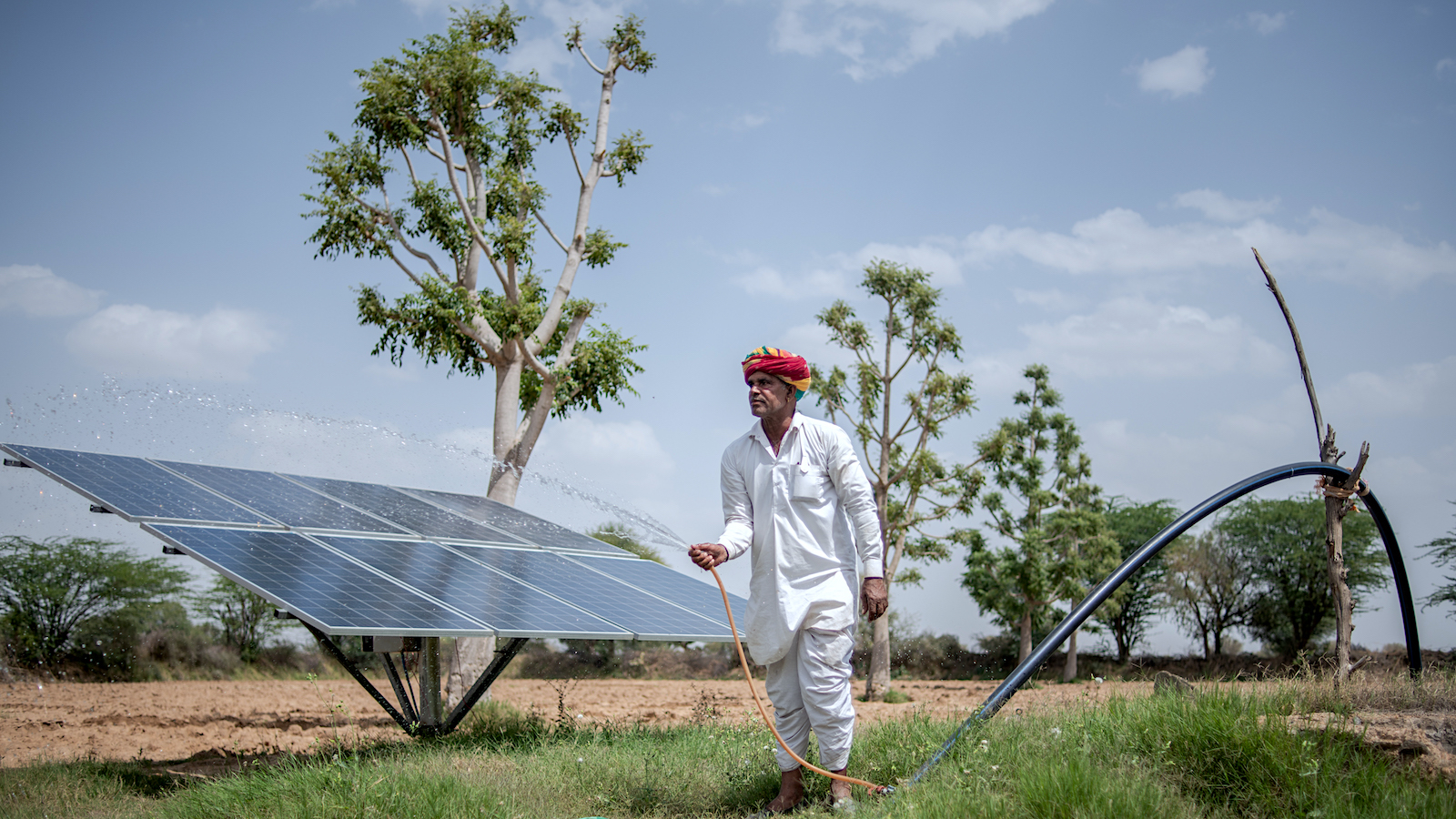

Innovative Solar-Powered Agriculture Techniques
Overview of Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems
Solar-powered irrigation systems use PV panels to power water pumps. They offer a cost-effective way to irrigate crops.
These systems are particularly useful in off-grid areas. They reduce reliance on diesel pumps, lowering costs and emissions.
Case Studies: Success Stories from Different Regions
In India, the Suryashakti Kisan Yojana (SKY) scheme provides subsidies for solar panels. Farmers use them to power water pumps.
This has led to increased crop yields and financial stability. Similar programs are being adopted worldwide.
Solar Drying and Cold Storage Solutions
Solar drying uses solar energy to dry crops efficiently. It reduces post-harvest losses due to spoilage.
Solar dryers provide a controlled environment. This improves the quality and shelf life of dried products.
Addressing Post-Harvest Losses with Solar Technology
Solar-powered cold storage units help preserve perishable goods. In regions with unreliable electricity, they maintain optimal temperatures.
This extends the shelf life of produce. It reduces food waste and increases farmers' incomes.
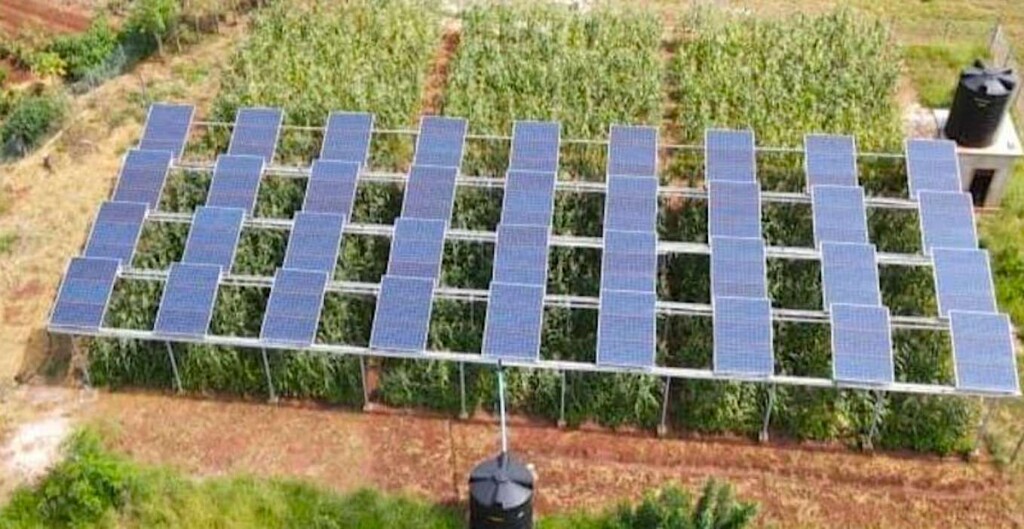
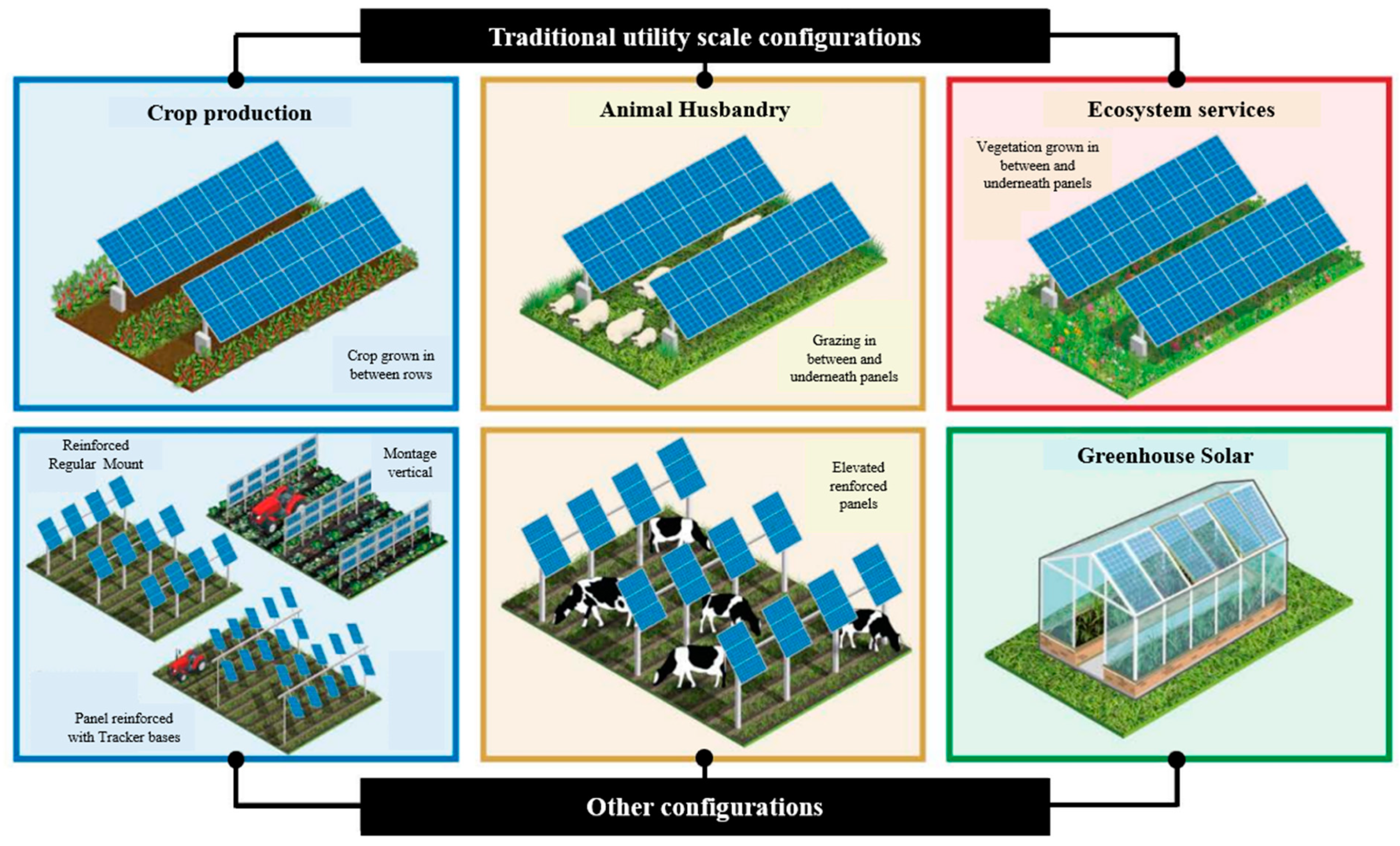
Agrivoltaics: Maximizing Land Use for Dual Benefits
Agrivoltaics involves installing solar panels above crops. This allows for simultaneous electricity generation and crop cultivation.
It maximizes land use and provides additional income. The shade from panels can also improve crop resilience.
How Agrivoltaics Works and Its Benefits
Solar panels are mounted at a height that allows crops to grow underneath. This provides shade and protection from extreme weather.
Agrivoltaics increases land productivity. It also creates new revenue streams for farmers.

Technological Innovations Supporting Solar Agriculture
Advancements in Solar Panel Technology
High-Efficiency Panels and Smart Farming Integration
Modern solar panels are more efficient and durable. Innovations like solar trackers and bifacial panels enhance energy production.
These technologies maximize sunlight use. They improve overall system performance.
The Role of IoT and Precision Agriculture
Enhancing Resource Management with Solar Energy
Combining solar energy with smart farming technologies optimizes resource use. Solar-powered sensors monitor soil moisture and adjust irrigation accordingly.
The Internet of Things (IoT) allows for automated farming operations. This enhances decision-making and increases productivity.
Challenges and Barriers to Solar Integration in Agriculture
Initial Investment Costs and Financing Options
The high upfront costs of solar installations can be a barrier. Financing options like subsidies, grants, and microloans help reduce these costs.
Pay-as-you-go models make solar energy more accessible. Farmers can pay in small installments.
Government Incentives and Subsidies
Governments offer incentives to promote solar adoption. These include tax credits, grants, and subsidies.
Such incentives make the investment in solar power lucrative. They encourage farmers to adopt sustainable practices.
Technical Knowledge and Training Needs
Importance of Extension Services and Support
Farmers need technical knowledge to install and maintain solar systems. Training programs and extension services are crucial.
They equip farmers with the necessary skills. Access to maintenance and support services ensures long-term success.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Need for Supportive Policies to Encourage Adoption
Supportive policies and regulations are essential. Governments should provide incentives and streamline approval processes.
Ensuring grid connectivity for surplus energy is also important. This maximizes the benefits of solar energy.
Future Trends in Solar Energy and Food Security
Innovations in Agrivoltaics and Sustainable Farming Models
The future of solar energy in agriculture looks promising. Innovations in agrivoltaics will enhance agricultural resilience.
As costs decrease and efficiency improves, solar energy will become more accessible. This supports the transition to sustainable agriculture.
The Role of Community and Cooperative Models in Solar Adoption
Community and cooperative models can play a significant role in solar adoption. Shared solar projects allow multiple farmers to benefit from a single installation.
These models reduce individual costs. They also foster collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Conclusion
Summary of the Synergetic Benefits of Solar Energy in Agriculture
Integrating solar energy into agriculture offers numerous benefits. It provides cost savings, environmental sustainability, and improved food security.
Solar-powered technologies address various agricultural challenges. They enhance productivity and resilience.
The Path Forward for Sustainable Food Systems
Harnessing solar energy presents an opportunity to revolutionize agriculture. By integrating advanced solar technologies, we can address food security, climate change, and economic stability.
Partnering with experts like 8MSolar can drive positive change. Together, we can cultivate a sustainable farming future that benefits all.
Key Takeaways:
- Solar energy significantly reduces farming costs and increases profit margins.
- Agrivoltaics maximizes land use by combining solar energy production with agriculture.
- Technological advancements and smart farming integration enhance resource management.
- Government incentives and supportive policies are crucial for widespread solar adoption.
- Community models and training programs can facilitate the transition to solar-powered agriculture.