AI Climate Predictions: A Faster Rise to 3°C
AI Predicts Accelerated Warming
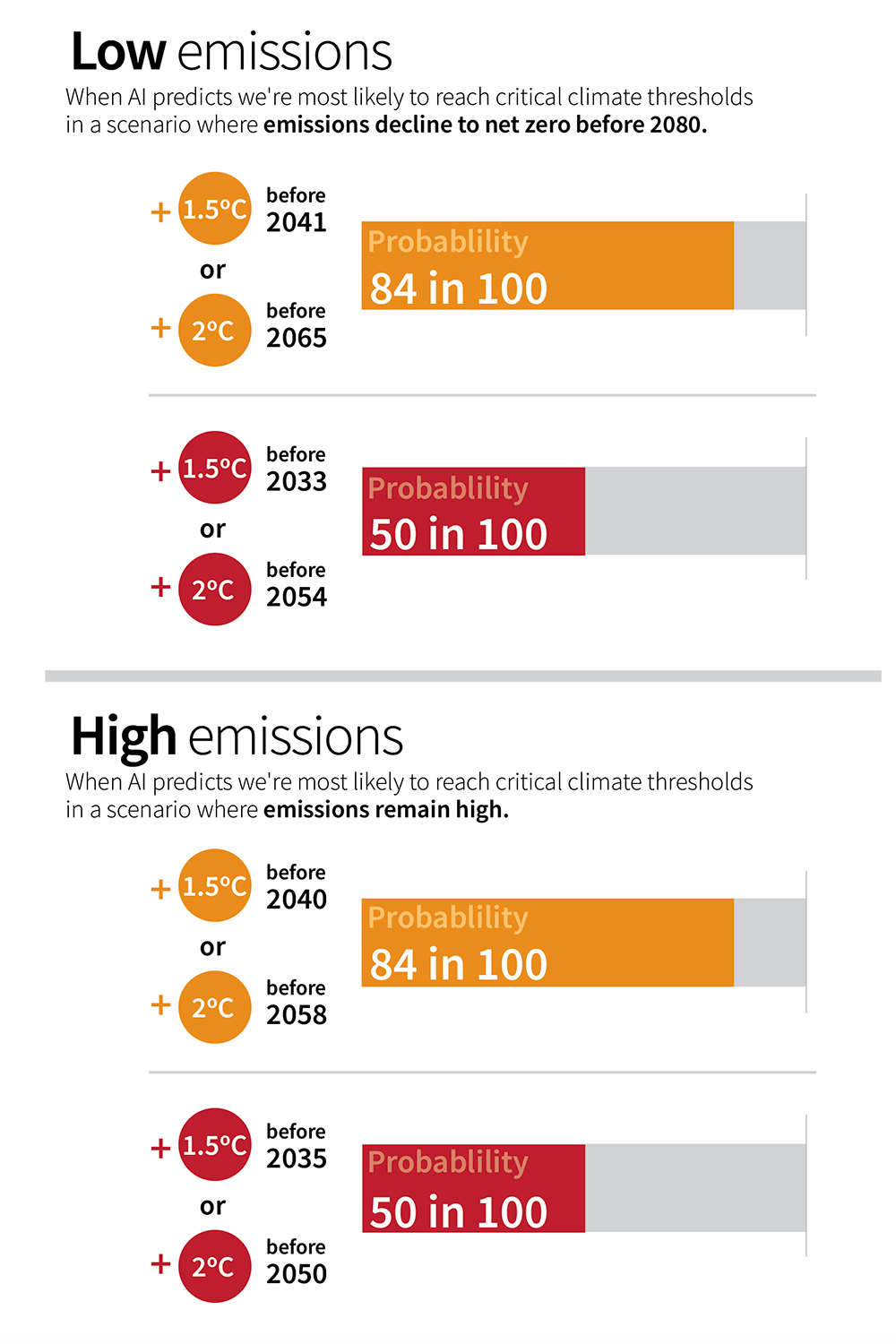
A recent study combining insights from ten global climate models and using artificial intelligence (AI) has revealed a concerning trend. Regional warming thresholds are likely to be reached faster than previously anticipated. This means that the critical 1.5°C warming mark could be surpassed by 2040 in many land regions, and a 3.0°C threshold may be crossed by 2060.
This accelerated timeline is significantly quicker than predicted in earlier studies. The research, published in Environmental Research Letters, highlights the urgent need for immediate climate action. The study was conducted by leading climate scientists Elizabeth Barnes, Noah Diffenbaugh, and Sonia Seneviratne.
Key Findings of the AI Climate Study
The study used a cutting-edge AI transfer-learning approach. This method integrated data from multiple climate models and observations. This resulted in more accurate regional predictions. The research revealed several key findings:
- 34 regions are likely to exceed 1.5°C of warming by 2040.
- 31 of these 34 regions are expected to reach 2°C of warming by 2040.
- 26 of these 34 regions are projected to surpass 3°C of warming by 2060.
These findings underscore the importance of using AI in climate modeling, according to Elizabeth Barnes. She noted that AI techniques like transfer learning can improve regional forecasts. This provides crucial insights for policymakers and communities.
Regions Facing the Most Rapid Temperature Increases
Certain regions are expected to experience these temperature increases more rapidly. South Asia, the Mediterranean, Central Europe, and parts of sub-Saharan Africa are particularly vulnerable. These areas face heightened risks to their ecosystems and communities.
The study emphasizes the importance of focusing on regional changes, not just global averages. Noah Diffenbaugh explained that regional climate change can be more uncertain due to various factors. These include atmospheric, oceanic, and land surface processes.
The Role of AI in Climate Modeling
AI is becoming an essential tool for refining climate projections. AI systems are trained using vast archives of climate model simulations. They then refine predictions with real-world observations. This approach helps to reduce uncertainty and improve the accuracy of climate forecasts.

AI can process large datasets and identify patterns that might be missed by traditional methods. This allows scientists to make more informed predictions about future warming trends. The integration of AI is crucial for better understanding and addressing the complexities of climate change.
Why Regional Focus is Critical
Focusing on regional changes is vital for effective climate action. Global temperature averages don't fully capture the specific impacts felt in different locations. Regional climate changes can vary significantly. This is why detailed, localized predictions are needed to anticipate and mitigate potential impacts.
Regional climate models can provide more precise information for local planning and adaptation strategies. Understanding regional variations is key to preparing for the specific challenges each area will face.
The Impact of a 3°C Temperature Rise
A 3°C temperature rise will have significant and far-reaching consequences. It will lead to more frequent and intense heat waves. This will put a strain on human health and increase energy demand.

The rise in temperature will also exacerbate droughts and wildfires. This will impact water resources, agriculture, and ecosystems worldwide.
Consequences for Cities
Cities are particularly vulnerable to the effects of a 3°C temperature rise. Many urban areas could face month-long heat waves. This would lead to skyrocketing energy demand for air conditioning.
A study by WRI found that the difference between 1.5°C and 3°C of warming is considerable in most cities. The risk of insect-borne diseases may also shift. Low-income communities will likely be the hardest hit.
Global Impacts of 3°C Warming
The global impacts of a 3°C warming will be severe. The planet could see a drastic increase in natural disasters. These include hurricanes, droughts, and heat waves. Sea levels will continue to rise, threatening coastal cities and communities.
Food production will also suffer, potentially leading to widespread shortages and malnutrition. Ecosystems will face severe disruptions, affecting biodiversity and natural resources.
The Need for Adaptation and Mitigation
Addressing the challenges posed by a 3°C temperature rise requires both adaptation and mitigation strategies. Adaptation involves taking steps to reduce vulnerability to climate change impacts. This includes investing in resilient infrastructure, developing drought-resistant crops, and improving public health systems.
Mitigation focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This can be achieved through transitioning to renewable energy sources and improving energy efficiency.
Investing in Adaptation Strategies
Investing in adaptation strategies is crucial for protecting communities from the worst effects of climate change. This includes developing early warning systems for extreme weather events. Improving water management practices can also help.
Adaptation measures also need to be tailored to local conditions. This will ensure that they are effective in addressing specific regional challenges.
The Importance of Decarbonization
Decarbonization is essential for mitigating climate change. This means transitioning away from fossil fuels and towards renewable energy sources. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is the most effective way to limit global warming.
Decarbonization efforts must be accelerated to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement. This requires both individual and collective action.
The Urgency of Climate Action
The latest AI-driven climate predictions underscore the urgency of climate action. The world is not on track to meet the Paris Agreement targets. Immediate and substantial efforts are needed to reduce emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
The window for meaningful action is closing. Delaying action will lead to more severe and irreversible consequences. The time to act is now.
Key Takeaways:
- AI predicts that many regions will reach 3°C warming by 2060, faster than previously estimated.
- South Asia, the Mediterranean, Central Europe, and parts of sub-Saharan Africa are particularly vulnerable.
- A 3°C rise will lead to more frequent heatwaves, droughts, and natural disasters.
- Adaptation and mitigation strategies are essential to address the impacts of climate change.
- Decarbonization is crucial to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and limiting global warming.
